Albert Szent-Györgyi
Background
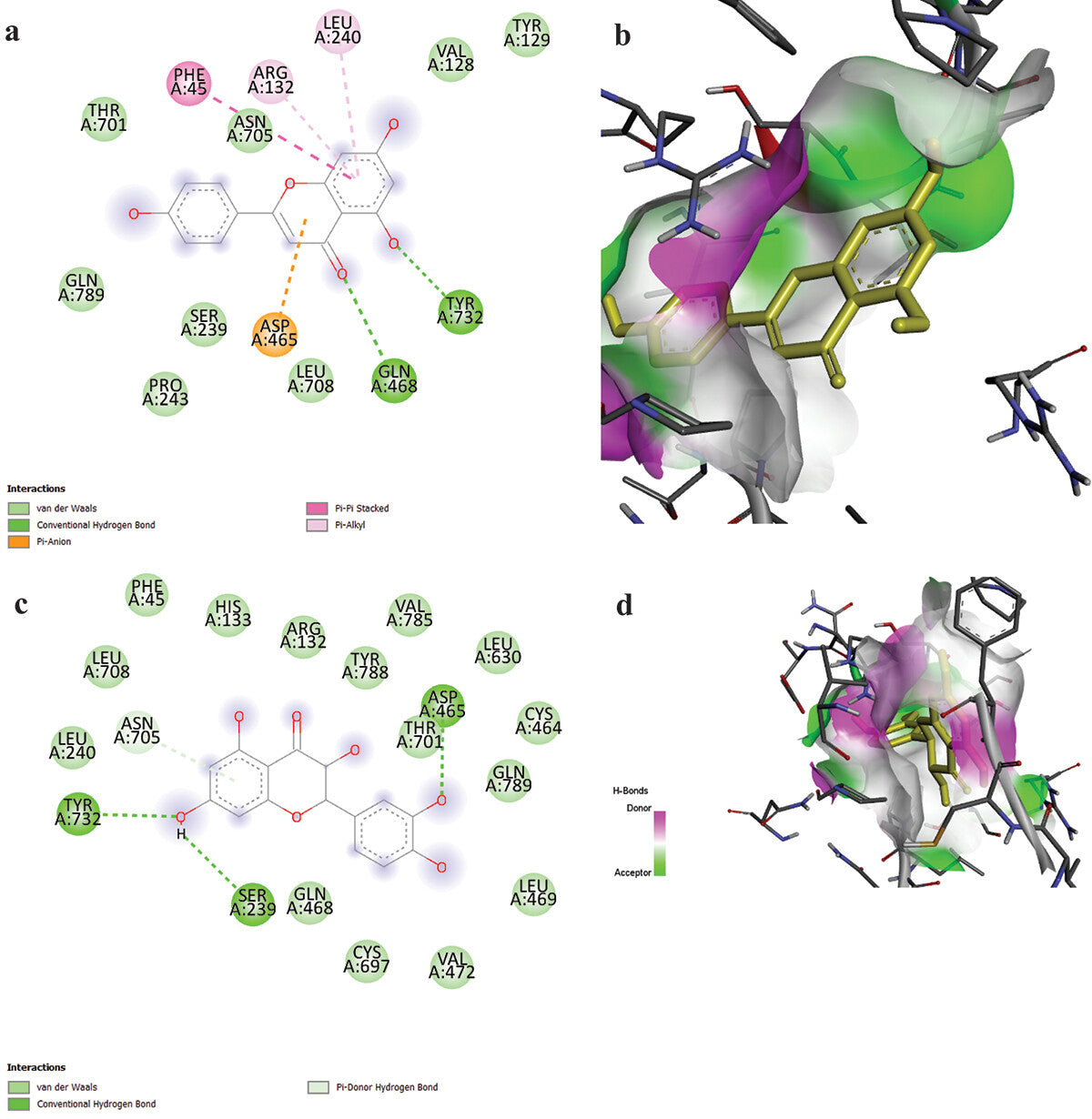
A new flavonoid
Taxifolin was first isolated and identified by the French chemist Jacques Masquelier in 1948. Albert Szent-Györgyi, a Hungarian physiologist, and biochemist, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1937 for his work on vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and its importance in human health. He also conducted research on flavonoids, including taxifolin, during his career. He initially referred to the flavonoids as vitamin P but it was later discovered that they are not essential to human health and therefore not technically vitamins.
Since then, taxifolin has been the subject of numerous studies exploring its potential health benefits, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, and anti-cancer properties. Albert Szent-Gyorgyi make significant contributions to the study of human health and nutrition.
Why VITA-P
Better bioavailability
VITA-P has been working on developing an aerosolized solution that can help to improve the absorption of taxifolin in the body. By improving bioavailability, VITA-P hopes to maximize the potential health benefits of taxifolin, and help individuals achieve better health outcomes. Through ongoing research and development, VITA-P is dedicated to unlocking the full potential of taxifolin as a natural dietary supplement.

Potential benefits
Why use inhaler
Pulmonary delivery
Inhalation aerosol technology allows rapid absorption into systemic circulation, delivering a more significant dose of Melatonin in a short amount of time. It's far more efficient than ingestion - a method of delivery that has random and sometimes poor bioavailability. In fact, ingested substances first pass through the metabolism and become less active than inhaled compounds that have direct access to the bloodstream without being metabolized first. Our products avoid first-pass metabolism and maximize bioavailability, allowing for a lower, safer active ingredient concentration.